Histology
| Embryology - 26 Apr 2024 |
|---|
| Google Translate - select your language from the list shown below (this will open a new external page) |
|
العربية | català | 中文 | 中國傳統的 | français | Deutsche | עִברִית | हिंदी | bahasa Indonesia | italiano | 日本語 | 한국어 | မြန်မာ | Pilipino | Polskie | português | ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ਦੇ | Română | русский | Español | Swahili | Svensk | ไทย | Türkçe | اردو | ייִדיש | Tiếng Việt These external translations are automated and may not be accurate. (More? About Translations) |
Introduction
Listed below are links to histology images and pages relating to different tissues and organs, the histology category will also display all the related content pages and media.
- histology - Links to all things histology.
- stains - List of stains and specific examples of the histology appearance. Histology sections, where the stain has been identified, link to this page and the specific stain description. For example: (Stain - Haematoxylin Eosin)
- Histology Glossary - Specialised glossary for histology terms and micro-anatomy.
- Category:Histology - Category listing pages and images associated with histology.
- ANAT2241 Histology - Support pages for undergraduate course.
- ANAT2511 Histology - Support pages for undergraduate course.
- UNSW Histology online virtual slide links (requires Moodle log-in).
Medicine
Foundations
SH Cycle A
- SH Lecture - Lymphatic Structure and Organs | Laboratory support Information
- SH Lecture - Respiratory System Development
BGD Cycle A
- BGDA Practical Histology of the female reproductive tract
- BGDA Practical Histology of the male reproductive tract
HM Cycle A
- HMA Practical Histology of blood vessels (practical 3)
- HMA Practical Cardiac Histology (practical 8)
AE Cycle B
- AEB Practical Histology of nervous system (practical 10) Audio
Science
- ANAT2511 - Fundamentals of Anatomy This course is designed as a stand‐alone subject for students who will benefit from knowledge of basic anatomy.
- ANAT2241 Histology - Basic and Systematic The aim of this course is to provide students with a thorough understanding of the microscopic appearance and function of normal structures in the human body.
Genital
Ovary Histology | Testis Histology | Spermatozoa Histology
Ovary Histology
Ovary histology: Tunica Albuginea x20 | Tunica albuginea, Germinal epithelium x40 | Primary follicle, primordial follicle, oocyte, x40 | Secondary follicle, cumulus oophorus, zona pelucida, granulosa cells, oocyte x20 | Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, Loupe | Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, x10 | Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, x40 | Corpus albicans, primary follicle, primordial follicle, granulosa cells, oocyte x20 | Menstrual Cycle | Ovary Development
Menstrual Histology
Uterine Endometrium
Vaginal Smear
Menstrual Cycle - Histology (images are listed in sequence and uterine endometrium from dilatation and curettage)
- Uterine Endometrium: menstrual | mid-proliferative | late proliferative | secretory | late secretory
- Vaginal Smear: early proliferative | mid-proliferative | late proliferative | secretory | late secretory
Links: Menstrual Cycle - Histology | Menstrual Cycle | Papanicolaou stain
Testis Histology
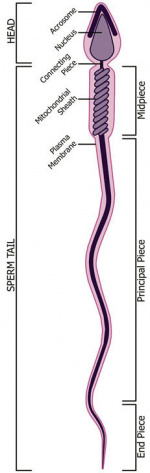
Testis Histology Links: Testis Development | Spermatozoa Development | Histology
- Human (young): overview labeled | overview unlabeled | convoluted seminiferous tubules x10 | x40 | x40 | tunica albuginea x20
- Human (adult): overview x2 | convoluted seminiferous tubules labeled | x10 | x20 | x40 | x40 | epididymis ductulus efferens | ductus epididymidis | epithelium | overview x4 | x10 | x20 | x40 | ductus deferens labeled overview | epithelium | overview x2 | x10 | x40
- Human Stage 22: Testis - labeled overview | Testis - unlabeled overview | Testis - unlabeled detail | Testis - labeled detail | testis | Carnegie stage 22 | Movie - Urogenital stage 22
- Mouse: postnatal epididymis | 14 days postnatal | 33 days postnatal | 45 days postnatal | 2 months postnatal
| Spermatozoa Development (expand to see terms) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Note there are additional glossaries associated with genital, spermatozoa, oocyte and renal.
See also: Spermatozoa Terms collapse table
|
Vaginal Smear Histology
- Smear Image Links: L. crispatus | L. crispatus | non-L. crispatus with thin lactobacilli | non-L. crispatus with thin lactobacilli | mixture non-L. crispatus with L. crispatus | mixture non-L. crispatus with L. crispatus | irregular-shaped Gram positive rod | irregular-shaped Gram positive rod | mixture Lactobacillus and bacterial vaginosis-associated | mixture Lactobacillus and bacterial vaginosis-associated | bacterial vaginosis | bacterial vaginosis
- Links: Menstrual Cycle - Histology | Histology - Gram Stain | Bacterial Vaginosis | CDC (USA) Fact Sheet - Bacterial Vaginosis
Endocrine
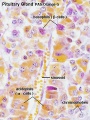
Pituitary Histology
- Pituitary Histology: Pituitary overview | Anterior H&E | Anterior H&E | Anterior labeled | PAS/O Overview | Acidophils | Basophils | Posterior labeled | Posterior unlabeled | Histology Stains | BGD - Endocrine Histology | Pituitary Development
Adrenal Histology
- Adrenal Histology: Cortex and Medulla | Unlabelled Overview | Cortical Zones | Zona Glomerulosa and Fasciculata | Zona Glomerulosa | Zona Fasciculata | Zona Reticularis and Medulla | Zona Reticularis | Medulla | Fetal Cortex | Developing Adult Cortex | BGD - Endocrine Histology | Histology Stains | Adrenal Development
Links: Histology | Histology Stains | Blue Histology images copyright Lutz Slomianka 1998-2009. The literary and artistic works on the original Blue Histology website may be reproduced, adapted, published and distributed for non-commercial purposes. See also the page Histology Stains.
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 26) Embryology Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
Cardiovascular
Blood
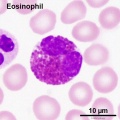
- Blood Histology: Blood Development | Blood Cell Number Table | Lymphocyte 1 | Lymphocyte 2 | Lymphocyte 3 | Lymphocyte 4 | Monocyte 1 | Monocyte 2 | Monocyte 3 | Monocyte 4 | Neutrophils 1 | Neutrophil 2 | Neutrophil 3 | Neutrophil 4 | Eosinophil 1 | Eosinophil 2 | labeled Neutrophil and Eosinophil | unlabeled - Neutrophil and Eosinophil | Basophil 1 | Basophil 2 | Basophil 3 | Platelet 1 | Platelet 2 | Reticulocyte | Megakaryocyte | Movie | Bone Marrow Histology | Category:Blood
| Blood Cells |
|---|
Adult human blood cell numbers shown in the table below is for reference purposes.
Blood Cell NumbersThe adult ranges of cells / 1 litre (l), total blood volume is about 4.7 to 5 litres. Blood Development | Blood Histology Red Blood Cells
Leukocytes (white blood cells)
Granulocytes
Non-Granulocytes
Lymphocytes
Platelets
|
Bone Marrow
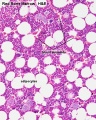
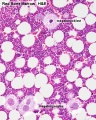
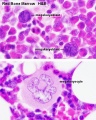
- Bone Marrow Histology: Blood Development | Marrow overview | Megakaryocyte | Megakaryocyte detail | Myelocyte | Normoblast | Reticulocyte | Blood Histology | Bone Development | Category:Blood
Heart
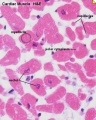
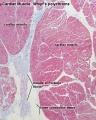
- Links: Heart Histology | Cardiac AZB Labeled | Cardiac AZB | Cardiac label LS | Cardiac LS | Cardiac label TS | Cardiac TS | Purkinje fibres | Purkinje fibres detail | Histology
Artery
Vein
Bone
Compact bone
Trabecular bone
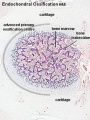
Endochondral ossification
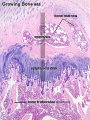
Intramembranous ossification
- Bone Histology: Cartilage Histology | Histology Stains | Histology | cartilage | bone | bone timeline
- Trabecular bone trabecular | lamellar | trabecular - overview HE | trabecular - low HE | trabecular - med HE
- Endochondral ossification primary ossification | endochondral ossification
- Intramembranous ossification intramembranous - VG low | intramembranous - VG high | intramembranous - HE low | intramembranous - HE high
Renal
Kidney
Ureter
Bladder
- Renal Histology: Histology | Histology Stains | Renal Development
- Kidney - Nephron overview | Glomerulus | Vascular and renal poles | Medullary ray | tubules
- Ureter - Ureter labeled | Ureter epithelium
- Bladder - overview | wall 1 | wall 2 | transitional epithelium | Urinary Bladder Development
Gastrointestinal Tract
Stomach
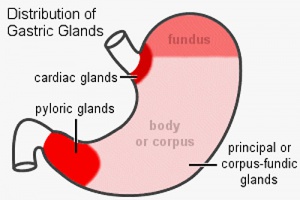
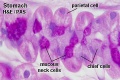
- Stomach Histology Links: stomach labeled overview | parietal cells - chief cells | mucus neck - parietal cells - chief cells | stomach overview | stomach mucosa | mucosa - secretory epithelial sheath - goblet cell | gastric glands - parietal cells - chief cells | stomach overview | Stomach Histology | Stomach Development | Gastrointestinal Tract Development
Intestine
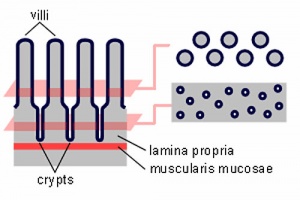
- Intestine Histology Links: Duodenum overview | Duodenum villi and crypts | Duodenum | Jejunum overview | Jejunum villus | Jejunum labeled | Jejunum unlabeled | Gastrointestinal Tract Histology | Intestine Development
Colon Histology
Liver Histology
- Liver Histology: Central vein (label) | Central vein (unlabel) | Portal triad 1 (label) | Portal triad 2 (label) | Portal triad (unlabel) | Hepatocytes (unlabel) | Hepatocytes polyploid (label) | Liver - reticular connective tissue (LP) | Liver - reticular connective tissue (HP) | Liver - fetal (HP) | Liver - fetal (HP) | Liver Development | GIT Histology
Gallbladder Histology
- Gallbladder Histology: overview (label) | overview (unlabel) | epithelium (label) | epithelium (unlabel) | GIT Histology
Respiratory
- Fetal Respiratory: late canalicular | unlabeled late canalicular | Hyaline cartilage | Respiratory Histology
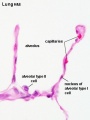
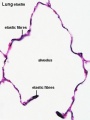
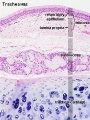
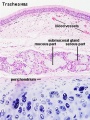
- Respiratory Histology: Bronchiole | Alveolar Duct | Alveoli | EM Alveoli septum | Alveoli Elastin | Trachea 1 | Trachea 2 | labeled lung | unlabeled lung | Respiratory Bronchiole | Lung Reticular Fibres | Nasal Inferior Concha | Nasal Respiratory Epithelium | Olfactory Region overview | Olfactory Region Epithelium | Histology Stains
Immune
Thymus
- Thymus Histology: Fetal Thymus overview | Fetal Thymus Medulla | Fetal Thymus Cortex | Adult Thymus | unlabeled fetal overview | unlabeled fetal medulla |unlabeled fetal thymic corpuscle |unlabeled fetal cortex | unlabeled adult overview | Category:Thymus | Immune System Development
Spleen
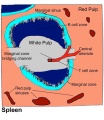
| Spleen Development: SH Lecture Spleen | SH Adult Histology | Overview Red and White Pulp | Overview Red and White Pulp | Cords and Sinuses | Reticular Fibre overview | Reticular Fibre detail | unlabeled red and white pulp | unlabeled red pulp and macrophages | unlabeled white pulp germinal centre | unlabeled reticular fibre | unlabeled white pulp reticular | unlabeled red pulp reticular | Structure cartoon | Cartoon and stain | Category:Spleen | Histology Stains | Immune System Development |
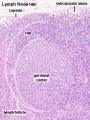
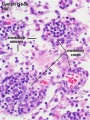
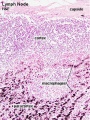
Lymph Node
- Lymph Node Histology: Subcapsular Sinus | Follicle | Germinal Centre | Medullary Cords and Sinuses | High Endothelial Venules | Macrophages | Node cartoons
- Lymph Node Cartoons: Detailed structure | Cartoon with Histology | Lymphocyte traffic | Simple structure | Simple node anatomy | Wiki node image | Internal structure | Mesenteric lymph node | Histology | Gallery | Lymph Node Development
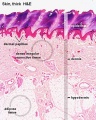
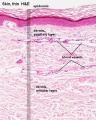
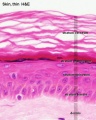
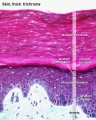
Integumentary
- Integument Histology Links: Adult Skin | Epidermis and Dermis | Thin Skin Epidermis | Thick Skin Epidermis | Elastic Fibres | Basal Cell Melanin | Foundations Practical Support | Integumentary System Development | Histology Stains
Labelled Pacinian corpuscle | Unlabelled Pacinian corpuscle | Unlabelled Pacinian corpuscle detail | Touch | Integumentary
Neural
Spinal Cord
- Spinal Cord: Overview 1 | Overview 2 | Overview animation | Grey matter | Grey matter | Grey matter | White matter | Overview unlabeled | Grey matter unlabeled 1 | Grey matter unlabeled 2 | White matter unlabeled 1 | Ependymal cells unlabeled
| Histology Links: stains | fixatives | artifacts | menstrual histology | placenta histology | heart histology | liver histology | Pancreas | Gall Bladder | Colon | Renal | Respiratory Histology | Bone | Category:Histology | UNSW Histology |
| Historic Histology Textbooks: 1941 Histology] | 1944 Oral Histology |
References
Singer C. (1914). Notes on the Early History of Microscopy. Proc. R. Soc. Med. , 7, 247-79. PMID: 19978172
Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004-2011. PMID 20641179 | Book Contents
Historic
Lewis FT. Stoehr's Histology. (1906) P. Blakiston's Son & Co., Philadelphia.
Lewis FT. and Stöhr P. A Text-book of Histology Arranged upon an Embryological Basis. (1913) P. Blakiston’s Son and Co., 539 pp., 495 figs.
Böhm AA. and M. Von Davidoff. (translated Huber GC.) A textbook of histology, including microscopic technic. (1910) Second Edn. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia and London.
External Links
External Links Notice - The dynamic nature of the internet may mean that some of these listed links may no longer function. If the link no longer works search the web with the link text or name. Links to any external commercial sites are provided for information purposes only and should never be considered an endorsement. UNSW Embryology is provided as an educational resource with no clinical information or commercial affiliation.
- NIH Common Fund Molecular Libraries and Imaging
- The History of Histology: A Brief Survey of Sources Bracegirdle, B. History of Science, Vol. 15, p.77-101 PDF
Glossary Links
- Glossary: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z | Numbers | Symbols | Term Link
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 26) Embryology Histology. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/Histology
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
![Corpus luteum, theca lutein cells, granulosa lutein cells, Loupe]](/embryology/images/thumb/1/1b/Ovary_histology_004.jpg/120px-Ovary_histology_004.jpg)



![Zona Glomerulosa and Fasciculata]](/embryology/images/thumb/6/67/Adrenal_histology_004.jpg/90px-Adrenal_histology_004.jpg)
![Developing Adult Cortex]](/embryology/images/thumb/0/05/Adrenal_histology_005.jpg/120px-Adrenal_histology_005.jpg)










![Ano-Rectal Junction Overview Labeled]](/embryology/images/thumb/5/52/Colon_histology_006.jpg/90px-Colon_histology_006.jpg)
![Colon Wall Labeled]](/embryology/images/thumb/e/ec/Colon_histology_001.jpg/90px-Colon_histology_001.jpg)

![Fetal Thymus overview]](/embryology/images/thumb/d/d6/Fetal_thymus.jpg/90px-Fetal_thymus.jpg)
![Fetal Thymus Medulla]](/embryology/images/thumb/5/58/Thymus_-_young_01.jpg/90px-Thymus_-_young_01.jpg)
![Fetal Thymus Cortex]](/embryology/images/thumb/1/1a/Thymus_-_young_02.jpg/90px-Thymus_-_young_02.jpg)