File:Nonmammalian VEGF Receptors.jpg
Original file (400 × 891 pixels, file size: 69 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
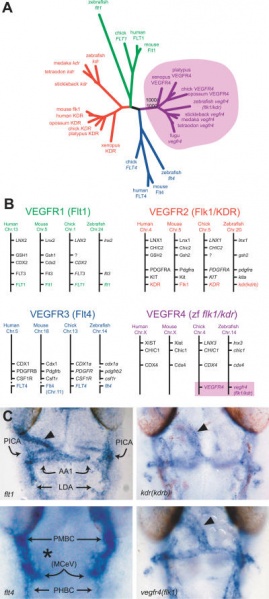
Zebrafish vegfr4(flk1) Represents a New Class of Nonmammalian VEGF Receptors
(A) Rooted neighbor-joining tree of vertebrate VEGF receptors. Different colors represent different classes of VEGF receptors. Note the clear separation of zebrafish and other teleost fish vegfr4, and the novel frog, chick, opossum, and platypus VEGF receptor genes from the three other classes of vertebrate VEGF receptors. Bootstrap value of VEGFR4 node is indicated (1,000 times out of 1,000 iterations).
(B) Synteny analysis of vertebrate VEGF receptors using human, mouse, chick, and zebrafish genome assemblies. Colors used are similar to those in (A). Question marks represent missing orthologous genes, potentially due to gaps in the chick genome assembly. Clear syntenic relationships of all vertebrate VEGF receptors were observed, indicating duplication from a primordial gene cluster in a primitive chordate. Mammals have lost the Zebrafish vegfr4 orthologue, coinciding with the emergence of the X-chromosome inactivation center XIST in the same genomic locus.
(C) Expression of zebrafish VEGF receptors in the heart region at 26 hpf, dorsal view, anterior to the top. Three VEGF receptors are expressed in the endocardium: vegfr4, kdr, and flt1 (arrowheads). Note the absence of flt4 expression in the endocardium (asterisk). At this stage, both vegfr4 and kdr are expressed at high levels in all endothelial cells, whereas flt1 and flt4 have a mutually exclusive expression pattern: flt1 is expressed in all arteries (AA1, first aortic arch; LDA, lateral dorsal aorta; and PICA, primitive internal carotid artery) whereas flt4 is expressed in all veins (MCeV, middle cerebral vein [which is largely out of the focal plane of this picture]). PHBC, primordial hindbrain channel; PMBC, primordial midbrain channel.
Reference
Bussmann J, Bakkers J & Schulte-Merker S. (2007). Early endocardial morphogenesis requires Scl/Tal1. PLoS Genet. , 3, e140. PMID: 17722983 DOI.
Copyright
© 2007 Bussmann et al.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
PLoS Genet. 2007 August; 3(8): e140. Early Endocardial Morphogenesis Requires Scl/Tal1 Jeroen Bussmann, Jeroen Bakkers, and Stefan Schulte-Merker PLoS Genet. 2007 August; 3(8): e140. Prepublished online 2007 July 9. Published online 2007 August 24. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030140.
Original File name: Pgen.0030140.g003.jpg
Cite this page: Hill, M.A. (2024, April 20) Embryology Nonmammalian VEGF Receptors.jpg. Retrieved from https://embryology.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php/File:Nonmammalian_VEGF_Receptors.jpg
- © Dr Mark Hill 2024, UNSW Embryology ISBN: 978 0 7334 2609 4 - UNSW CRICOS Provider Code No. 00098G
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 11:11, 15 August 2009 |  | 400 × 891 (69 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Zebrafish vegfr4(flk1) Represents a New Class of Nonmammalian VEGF Receptors (A) Rooted neighbor-joining tree of vertebrate VEGF receptors. Different colors represent different classes of VEGF receptors. Note the clear separation of zebrafish and other t |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following 2 pages use this file: