File:Mitosis and meiosis.jpg
Original file (1,000 × 423 pixels, file size: 58 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
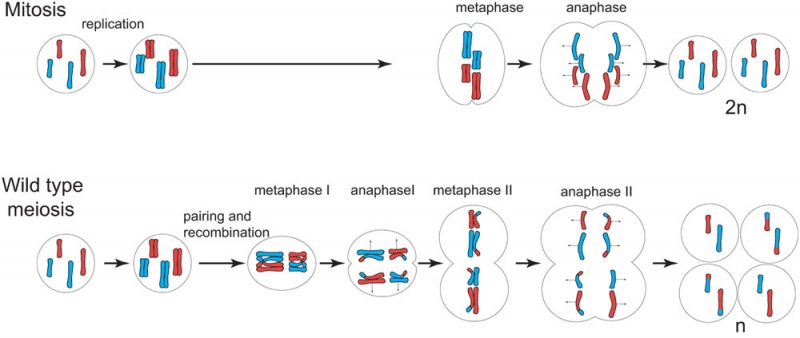
Mitosis and Meiosis
During mitosis in diploid cells, chromosomes replicate and sister chromatids segregate to generate daughter cells that are diploid and genetically identical to the initial cell. During meiosis two rounds of chromosome segregation follow a single round of replication.
- At division one, homologous chromosomes recombine and are separated.
- Meiosis II is more similar to mitosis, resulting in equal distribution of sister chromatids.
Reference
<pubmed>19513101</pubmed>PMC2685454 | PLoS Biol.
Copyright
© 2009 d'Erfurth et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Citation: d'Erfurth I, Jolivet S, Froger N, Catrice O, Novatchkova M, et al. (2009) Turning Meiosis into Mitosis. PLoS Biol 7(6): e1000124. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000124
Modified from Figure 1 sexual plant Arabidopsis thaliana.
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 17:45, 27 July 2010 |  | 1,000 × 423 (58 KB) | S8600021 (talk | contribs) | Mitosis and Meiosis Modified from Figure 1 sexual plant Arabidopsis thaliana During mitosis in diploid cells, chromosomes replicate and sister chromatids segregate to generate daughter cells that are diploid and genetically identical to the initial cel |
You cannot overwrite this file.